Robotic process automation (RPA)
According to a survey by Gartner, 75% of controllers would like to use RPA but only 19% are. There's a fear around automation that it will take someone's job, however it only takes pieces of a person's time, and by freeing those people to do other things, they can focus more on analytics. When robots and workflows do the number-crunching, finance staff can focus on providing high-level insights that drive business decisions and enable growth.
RPA can help finance functions to improve the accuracy and efficiency of critical business processes. It also establishes a strong foundation for organisations to move onto the next step of the automation journey, where more sophisticated technologies such as artificial intelligence can be adopted to deliver transformational change.
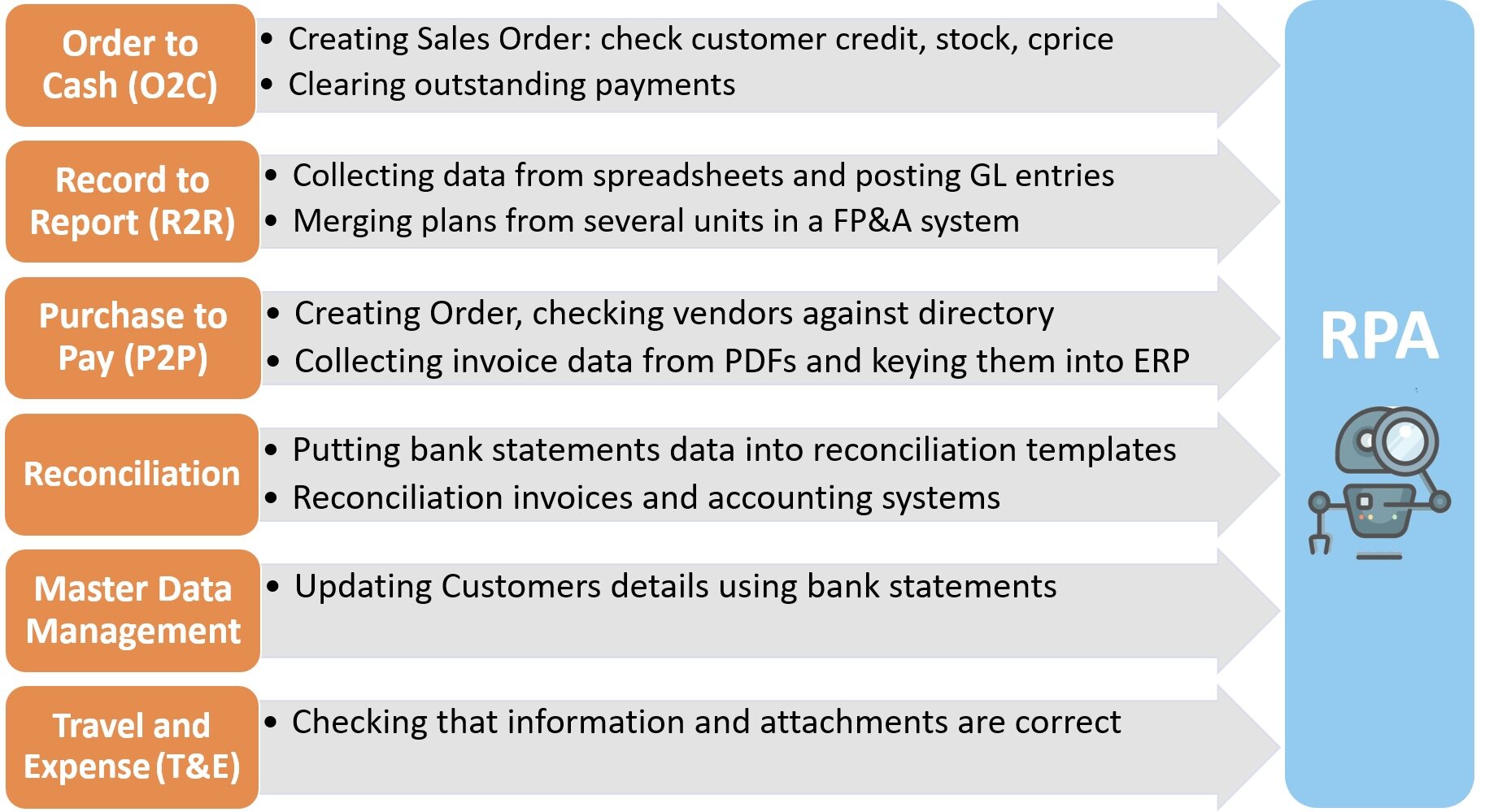
Robotic process automation (RPA) use cases in accounting:
Accounts Payable (AP)
Accounts Receivable (AR)
Reconciliations
Cost allocation
Financial close & reporting
A McKinsey report confirms, by estimating a global automation potential of 43% for finance and accounting. Relatedly, UiPath specifies an automation rate of 80% for common processes like accounts receivable or accounts payable.
Automation can help reduce human errors in an AR process and optimize the way your company approaches collections, reconciliation and the entire enterprise cash cycle. Robotic Process Automation increases efficiency by 44% by automating manually repetitive tasks. (Digital Workforce, 2019)
A Deloitte study revealed that organizations that have adopted RPA found success in improved compliance (92%), improved quality/accuracy (90%), improved productivity (86%) and cost reduction (59%).
RPA Benefits/ Results of implementation:
Financial benefits
By 2024, organizations will lower operational costs by 30% by combining hyper-automation technologies with redesigned operational processes. (Gartner)
Organizations that have piloted RPA expect, on average, a 9-month payback period while, in reality, the payback achieved by those that have implemented and scaled RPA has been 12 months. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
There is an expectation that robots could deliver a significant portion of current transactional activities. On average, the expectation is that 20% of FTE capacity could be provided by robots. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
This expectation matches the reality for those that have already implemented RPA. In fact, those that have scaled RPA appear to have had such a positive experience that their expectations are even more ambitious: they believe that 52% of FTE capacity could be provided by robots. This can enable the human workforce to be redeployed to more value-adding activities. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
RPA can reduce labour-intensive tasks by 80%. (Automation Anywhere)
Top performers earned nearly 4X on their RPA investments, while other enterprises earned nearly double. (Everest Group)
RPA can provide cost savings ranging from 20%–60% of baseline FTE costs for financial services. (EY)
Other benefits
85% of respondents report that RPA met or exceeded their expectations for non-financial benefits such as accuracy, timeliness, flexibility. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
More than 50% of C-level executives using intelligent automation have identified key operational processes that can be augmented or automated using AI capabilities. (IBM)
38% of managers report compliance improvements are the leading benefit of RPA and it is followed by improved productivity/performance (27%) (NICE)
RPA Challenges
Only 3% of organizations have scaled their digital workforce. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
The time and cost to deliver RPA tend to be underestimated by organizations. 63% said their expectations of time to implement were not met and 37% said their expectations of cost to implement were not met. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
Only 17% of respondents faced some employee resistance when it comes to piloting RPA. This dropped to only 3% with respondents who were implementing or scaling RPA. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
For the majority of organizations (63%), implementation will involve working alongside a dedicated third-party partner due to a lack of specialist skills. (Deloitte Global RPA Survey)
Most executives believe that their organization does not have the necessary data science, machine learning and other AI/cognitive skills for process automation. Percentages of executives who think their lack specific skillset for each automation capability are:
90% for basic process automation
89% for advanced process automation
75% for intelligent process automation (IBM)
Only 20% of executives surveyed have yet to establish plans to retrain or reskill their workforce. (IBM)